Describe the Structure and Function of the Placenta
The placenta is a unique organ found only in mammals that allows the mother to provide a very large amount. This is a disc which is embedded in the uterine wall which contains villi on the embryo side of the tissue and on the mothers side are blood spaces which surround the villi.

Embryonic Development Anatomy And Physiology Ii
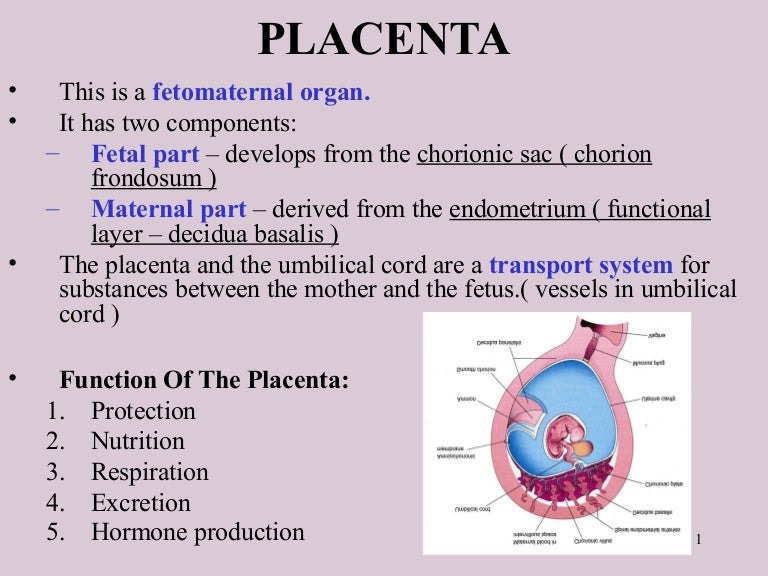
On fetal side the placenta is bordered by chorionic plate and on its maternal side by decidual plate In the junctional zone trophoblast and decidual cells intermingle it consists of giant syncitial and decidual cell At this stage most of the.
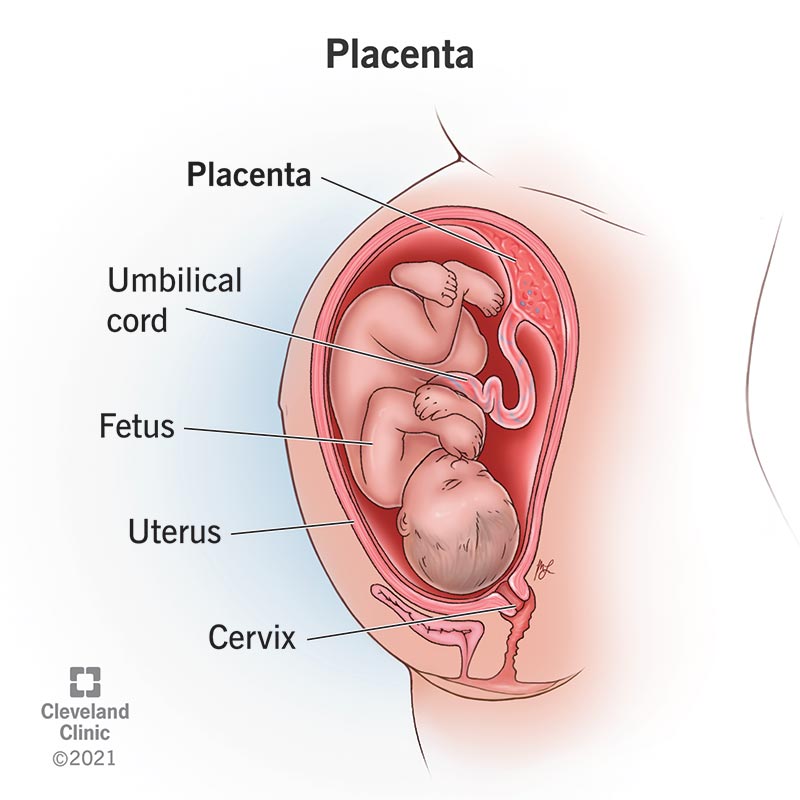
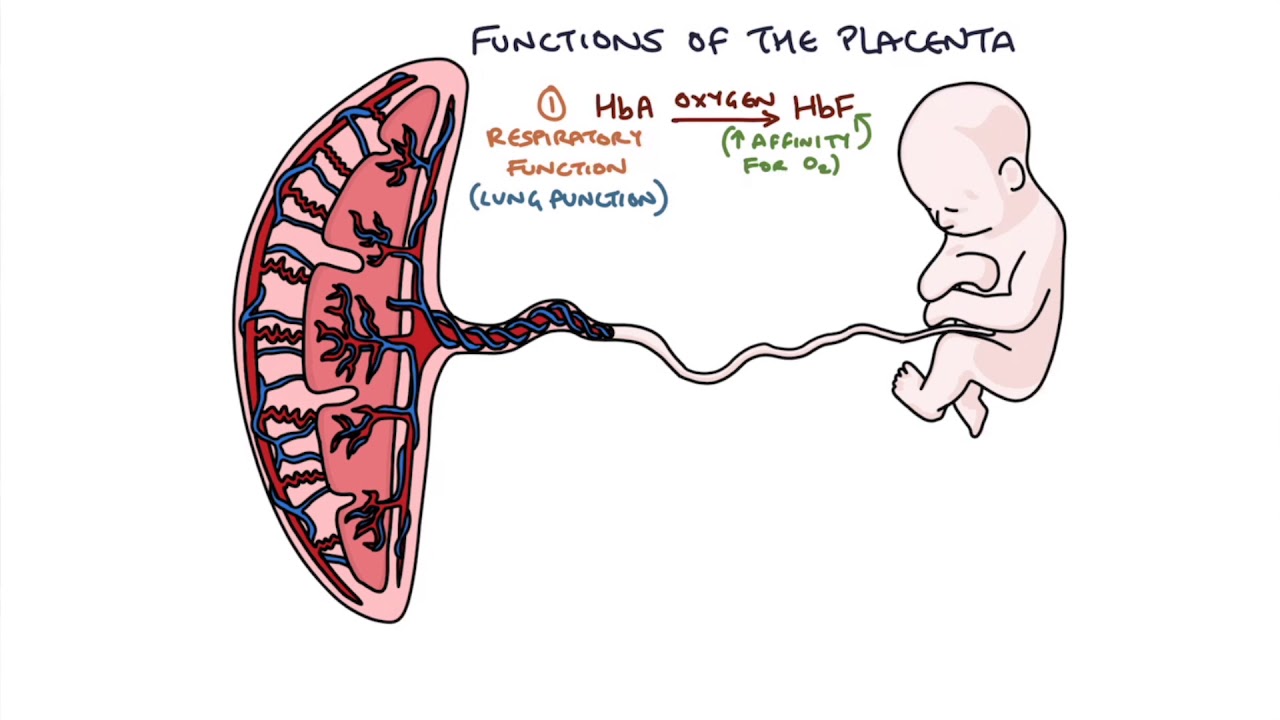
. It is an organ of exchange that provides oxygen and nutrients to fetus and removes waste produced by fetus. From the outer surface of the chorion a number of finger like projections known as chorionic villi grow into the tissue of the uterus. The placenta offers oxygen nutrients to the growing baby and it removes waste products from your babys blood.
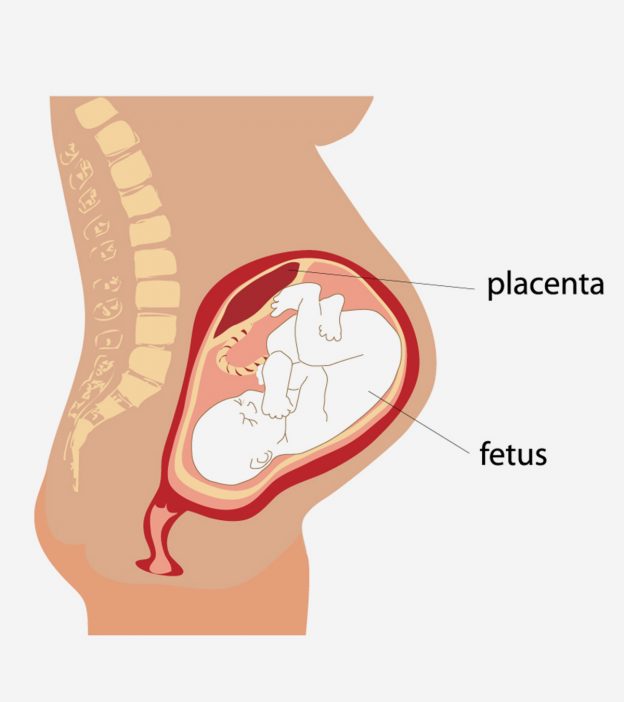
Each lobule acts as an independent maternal -fetal exchange unit. At term the placenta weighs almost 500 g has a diameter of 1520 cm a thickness of 23 cm and a surface area of almost 15 m 2. The placenta is a disc-shaped organ which provides the sole physical link between mother and fetus.
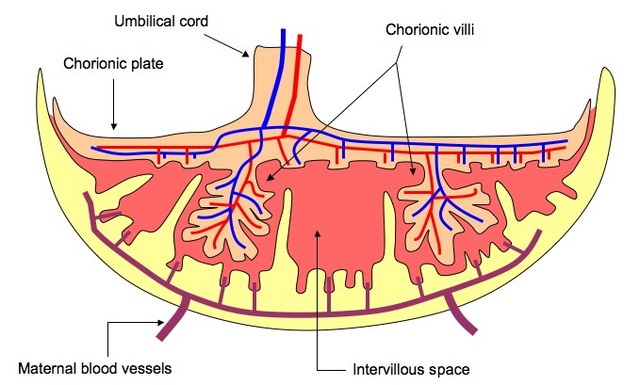
A number of finger-like projections known as chorionic villi grow into uterine tissue from the chorions outer surface. - delivery of gases. Placentation is the process of forming the placenta the site of exchange of nutrients and wastes between the mother and fetus.
From the outer surface of the chorion a number of finger like projections know as chorionic villi grow into the tissue of the uterus. It allows for the exchange of gases and nutrients between mother and fetus. It also removes metabolic wastes from the embryo.
In general the placenta is located in the fundus the top of the mothers uterus. Secretion of steroid and peptide hormones cytokines and growth factors. Based on the developmental stage villous structure vessel branches histologic features and vessel-cell type components at least five types of villi have been described.
The placenta also produces hormones needed to sustain the pregnancy The placenta is unique because it develops from two separate individuals the mother and the fetus. The placenta has multiple functions that are fundamental for the proper development of the fetus. Placenta is a structure that establishes firm connection between the foetus and the mother.
Structure Placenta is a disc-like structure embedded in the Uterine wall. However sometimes it can insert itself in other areas. The villi are arranged into a series of 30- 40 lobules each centred over the opening of a spiral artery.
- control of toxic substances. It is associated with the viviparity of the organism. It also serves as source of progesterone and estrogen hormones.
It is a disc like structure embedded in the uterine wall connected to the embryo. The functions of the placenta. During pregnancy the placenta grows to provide an ever-larger surface area for materno-fetal exchange.
It contains blood spaces on mothers side which surround the villi. Placenta is the link between the mothers body and the baby embryo. It is consists of numerous villi that increases the surface area for absorption.
It has villi on the embryos side of the tissue and on the mother side it has blood spaces which surrounds the villi. Structure of Placenta. These villi penetrate the tissue of the uterine wall of the mother and form placenta.
Function of Placenta. These villi pierce the mothers uterine wall and create the placenta. Describe the structure and function of the placenta.
Villous trees are the main structure of the placenta. These villi penetrate the tissue of the uterine wall of the mother and form. Placenta is a disc like structure that forms a connection between the embryo and the uterine wall.
Describe the structure and function of placenta 2 See answers Advertisement Advertisement shashanksen16 shashanksen16 Placenta is the composite structure of embryonic and maternal tissues that supplies nutrients to the developing embryo. It develops in the uterus during pregnancy It attaches to the wall of the uterus and the babys umbilical cord arises from it. Fetal portion Maternal portion 3.
- delivery of nutrients. Structure of placenta At start of fourth monthplacenta has 2 components. Describe the development of the placenta in the 3rd trimester in response to higher fetal need there is a second burst of angiogenesis exisiting blood vessels elongate in restricted space leading them to coil and bulge out - this pushes out villous tissue and creates terminal villi.
An illustration of the architecture of different villous trees is shown in Figure 31A. Structure of Placenta. The placenta serves three main functions.
It is a disc like structure embedded in the uterine wall connected to the embryo. It has villi on the embryos side of the tissue and on the mothers side it has blood spaces which surround the villi. - immunological function to prevent rejection of.
Placenta types structure function development abnormalities. - storagereservoir of energy. The placenta is a structure that forms a strong bond between the fetus and the mother.
It helps in nourishment of the embryo. The placenta is the composite structure of embryonic and maternal tissues that supply nutrients to the developing embryo. The placenta is a connection between foetal membrane and.
The placenta in humans is chorionic as it is made of the chorion membrane of extra-embryonic membrane. The placenta is a disc-shaped organ which provides the sole physical link between mother and fetus. Describe the structure and functions of the placenta.
Attach the fetus to the uterine. The placenta is more than a gas exchanger. It contains villi on the side of the embryo.
It provides a large surface area for glucose and 0 2 to pass from mothers blood to the embryo. - produce placental derived hormones. - excretion of waste products.
Placenta is a special tissue that helps human embryo in obtaining nutrition from mothers blood. Terms in this set 29 Describe the functions of the placenta. Placenta is a temporary membrane that connects the foetus and the mother mechanically and physiologically to provide nutrition help in respiration and excretion.
6 Functions Of Placenta During Pregnancy Symptoms Problems

Basic Structure Of The Placenta Showing Maternal And Fetal Sides And Download Scientific Diagram

Placenta What Is It And How It Works Biology Dictionary

What Is The Placenta Placenta Development Location Function Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

The Structure And Function Of The Placenta Ib Biology Youtube

The Placenta Is The Structure Formed A By The Union Of Fetal And Uterine Tissue B By Fetus Only C By Fusion Of Germ Layers D None Of These Study Com

Solved What Is Placenta Describe Its Structure State Its Func Self Study 365

The Placenta Structure And Function 2 Lectures Flashcards Quizlet

Functions Of The Placenta Anaesthesia Intensive Care Medicine

Igcse Biology 2017 3 11 Describe The Role Of The Placenta In The Nutrition Of The Developing Embryo

Placenta Structure And Functions Explained With Diagram

Structure Of The Mouse Placenta The Mature Placenta E14 5 Consists Download Scientific Diagram

Describe The Structure And Function Of Placenta Brainly In

Describe In Brief The Structure And Function Of Placenta Flash Education

Comments
Post a Comment